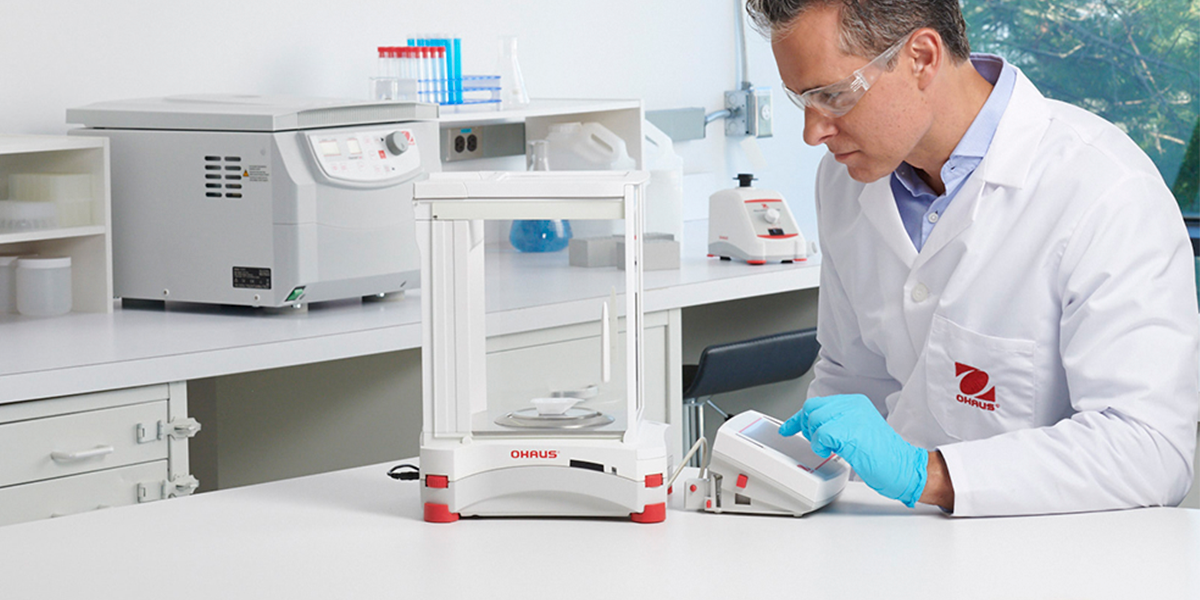
What is a laboratory balance?
A laboratory balance or scale is a balance suitable for the use within a laboratory environment. The requirements concerning reliability and performance for a laboratory balance are a lot higher than for example a household scale. Different types of laboratory balances are defined based on their readability: ultra-micro balances, micro-balances, semi-micro balances, analytical balances, and precision balances.
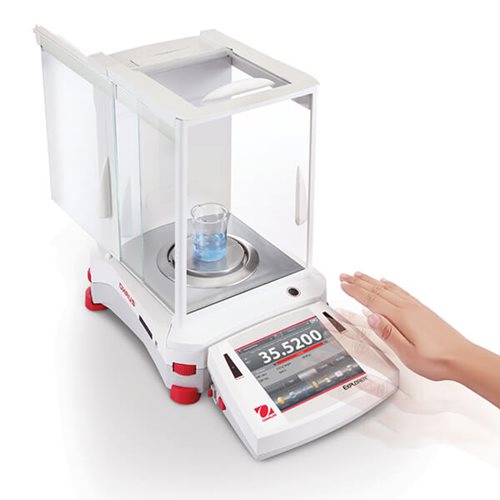

What is a semi-micro balance?
A semi-micro balance is a balance with a readability of 0,01 mg. It is often used to measure very low quantities of sample with a demand for a very good repeatability. This type of balance always has a draft shield and readability of 0,01 mg. The weighing platform is round with a diameter around 80 mm.
The capacity (max weight) : between 50 and 120 g.
Sometimes they also have a built-in ionizer to eliminate the effect of electrostatic charges.

What is an analytical balance?
An analytical balance is a balance with a readability of 0,1 mg. This type of balance always has a draft shield. The weighing platform is typically round with a diameter of about 90 mm.
The capacity: between 100 and 350 g.

What is a precision balance?
A precision balance is a balance with a readability of 0,001; 0,01 or 0,1 g. The balances of 0,001 g often come with a draft shield. The balances of 0,01 and
0,1 g come without draft shield. The weighing platform can be round or rectangular.
The capacity: between 220g and 35 kg.
How do laboratory balances work?
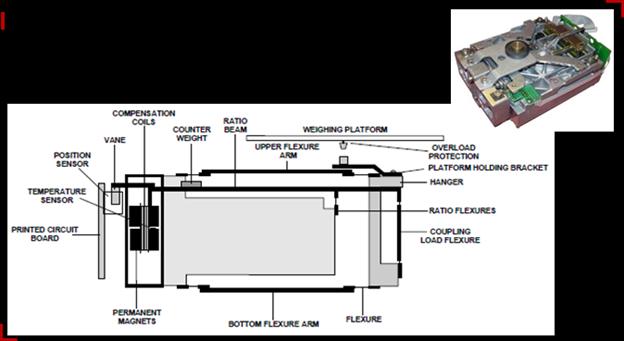
Most laboratory balances use a weighing cell with electromagnetic compensation. For this type of load cell, a leverage is used. One side of the leverage is connected to the weighing platform. The other side is connected to a coil. The coil is positioned around a magnet and is electromagnetic itself. The electromagnetic force of the coil depends on the amount of power that is send through it. When there’s a sample on the weighing platform, the leverage will move the coil upwards. The balance will try to move the coil back to the same position by increasing the power sent through the coil. This will increase the electromagnetic force. The amount of power needed to move the coil back to its original position is in direct relation with the mass of the sample. The controller of the balance will use the needed power to calculate and display the mass of the sample.
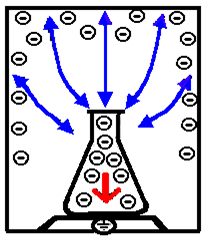
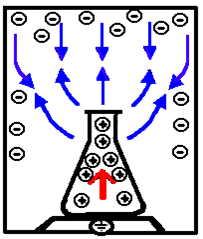
What is an Ionizer?
Electrostatic charges or static electricity are caused by friction on objects with a low conductivity and a high surface. Typical examples are plastic and glass weighing boats. The draft shield of the balance is often constructed of glass and plastics and has a negative charge. When the sample or weighing boat has an electrical charge, there will be a repulsion or attraction due to the load on the draft shield. This will create an upward or downward force that can affect the weighing results.
The use of an ionizer
There are different ways to counteract this effect. One of the most important ones is the use of an ionizer. An ionizer will create positive and negative ions. When a sample is loaded, the ions of the opposite charge will neutralize the charge of the sample/ weighing boat.
What is a moisture balance?
A moisture balance or moisture analyzer is an instrument to measure the moisture content or dry content of a sample. The principle used is thermogravimetry. The technology uses a precision balance and a heating element. The heating element (halogen lamp or metal infrared heater) dries the sample. The precision balance weighs the sample during the drying process. If there is no or little moisture loss detected, the moisture balance can calculate the moisture content or dry content based on the weight difference. The main advantage of this technology is its speed: you can determine the moisture content of a sample in a few minutes, while classical methods with a drying oven usually
take hours or even days. Learn more
What is a powder weighing cabinet?
The ideal solution for hazardous weighing operations.
ERLAB secure weighing station guarantees an outstanding level of safety for users. It provides the required stability as well as the level of accuracy (up to 10-6 g) required when weighing in the laboratory. It is the ideal solution for hazardous operations which require a confined environment, eliminating any risk of personnel being exposed to toxic products.