Prostate Cancer Detection - PSA testing - Prostate Health Index (phi)
What is phi ?
An FDA-approved blood test to be used as an aid in distinguishing prostate cancer from benign prostatic conditions
The Prostate Health Index (phi) is a calculation that uses a combination of three blood tests to produce a "phi score." This score provides more information about what elevated PSA levels might mean and the probability of finding prostate cancer on biopsy.*
phi is three things: a simple blood test to
improve early detection of prostate cancer, a tool to reduce negative
biopsies and provide more confidence in your biopsy decisions, and it is
used as a recommendation by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
(NCCN) Guidelines for PCa Early Detection prior to transrectal
ultrasound (TRUS) guided biopsies.
phi comprises three tests in combination:
PSA free PSA p2PSA
The new p2PSA assay specifically measures [-2]proPSA. The [-2]proPSA biomarker is an isoform of free PSA that was identified as the most prostate cancer-specific form found in tumor extracts.1 The PSA, free PSA and p2PSA results are combined in the Access instrument to calculate a probability of prostate cancer.
Benefits of phi Testing
The PSA test is a widely used screening tool for prostate cancer. However, given the PSA test’s limited specificity for cancer, a more precise tool is needed for prostate cancer detection. The phi score provides better risk stratification to identify patients who need a biopsy.† The appropriate use of phi can significantly modify physicians behavior patterns and improve their ability to diagnose and manage their patients. phi is another tool to help their patients decide if a biopsy is right for them.
The power of phi
A recent study published in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases demonstrated that physicians elected to perform fewer prostate biopsies for men who presented in the diagnostic gray zone when phi testing was included in their overall routine clinical assessment. Physicians reported that phi testing significantly impacted their patient management decision in over 73% of their cases.
How is the phi analysis used in clinical practice ?
The phi test helps determine the risk of prostate cancer and is intended to fill the diagnostic gap between PSA screening and prostate biopsy.
Closing the Diagnostic Gap
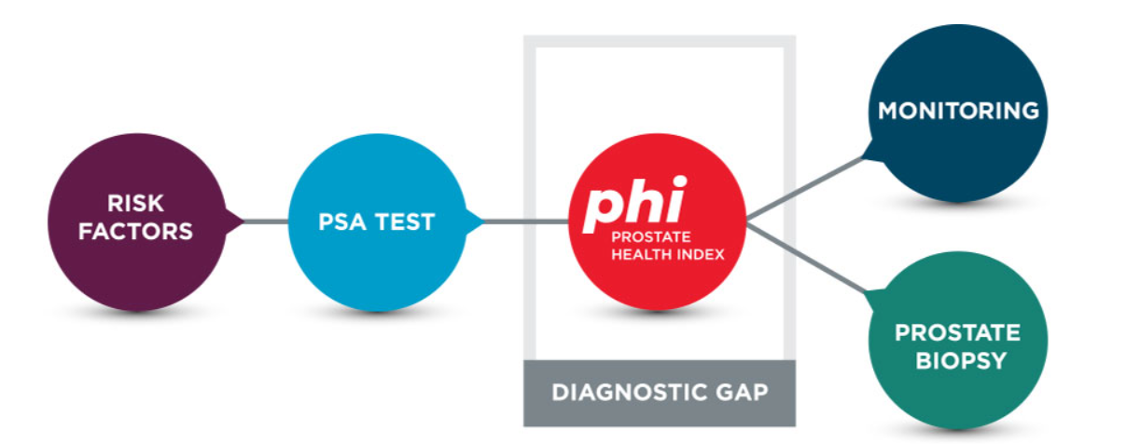
Figure: Identify the risk factors of prostate cancer and fill the diagnostic gap with a phi test for diagnosis and monitoring.
*By offering
phi
as part of prostate cancer testing for patients with non-suspicious DRE findings and tPSA in the 4-10 ng/mL range, clinicians can:
- Gain greater specificity through the addition of p2PSA in diagnostic testing
- Potentially reduce negative or unnecessary biopsies through increased specificity11
What does phi score mean ?
Table 1 represents clinical study data analyzed to estimate an individual patient's probability of having detectable prostate cancer based on Beckman Coulter phi results when that patient has a PSA in the diagnostic gray zone between 4 and 10 ng/mL.3 At phi cutoffs between 27 to 55, the probability of cancer ranged from 16.8 to 50.1%.‡ For example, a patient with a phi result below 27 has a 90% chance that his prostate biopsy will be negative.
Table 1. Probability of Prostate Cancer Based on phi Results Between 4 and 10 ng/mL1
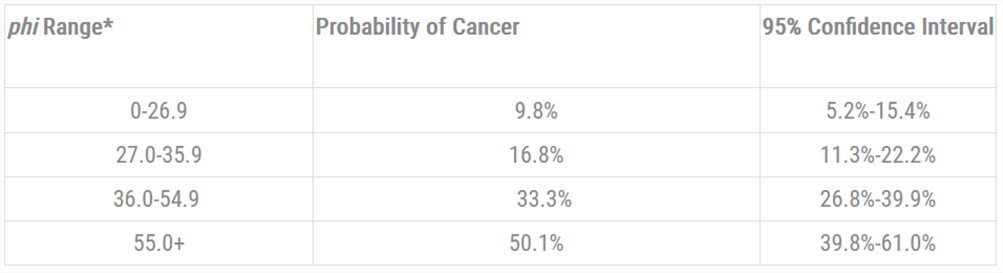
Clinical study data shows phi results can be used to assess probability of cancer.
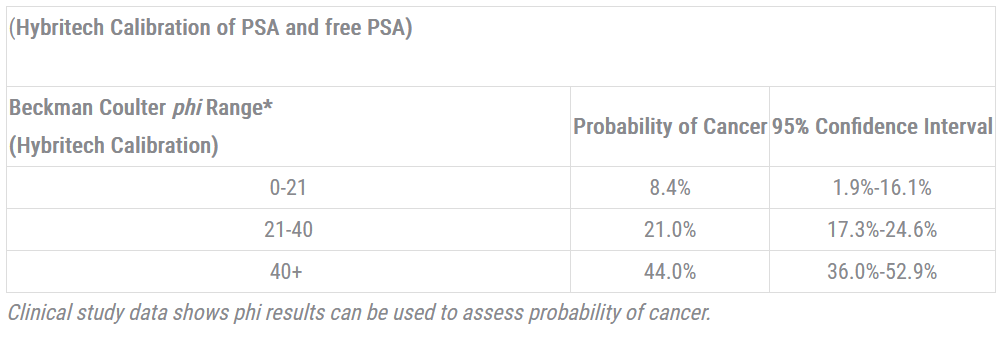
The phi diagnostic gray zone in countries outside of the U.S.and China is defined as PSA levels between 2 and 10ng/mL. The probability slightly changes based on these PSA levels (see Table 2).
Table 2. Probability of Prostate Cancer Based on phi Results Between 2 and 10 ng/mL2
FAQ
- How Prevalent is Prostate Cancer?
- What Tests are Used in Prostate Cancer Detection?
- Are PSA Tests Accurate for Assessing Risk of Prostate Cancer?
- How do Biopsies Impact Patients and the Healthcare Industry?


